Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix is an acellular human dermis graft sterilized using the Tutoplast® Tissue Sterilization Process. This proprietary process retains the three dimensional intertwined multidirectional fibers and mechanical properties of the native tissue. Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix provides a natural scaffold to support the body’s regenerative processes.

Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix at a Glance
STERILE
Terminally sterilized to a Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) 10-6 Via the Tutoplast Process
BIOCOMPATIBLE
- Preserved vascular channels
- Preserved key components of the native matrix
- Revascularization evident in as early as 7 days in an animal model
CONVENIENT
- Five year shelf life
The Tutoplast Process uses solvent dehydration to allow for a five year on-the-shelf storage. This proprietary processing step eliminates the need for freezing or refrigeration of the graft. The storage characteristics of Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix provide convenient, on-the-shelf storage between 1 °C and 37 °C for easy access and use.
- Simple single step rehydration
Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix’s single rehydration step* in room temperature sterile saline requires minimal effort and time. The quick rehydration of the Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix can reduce OR time and costs

The Tutoplast Process is a validated chemical sterilization methodology specifically developed to sterilize and preserve tissue for implantation.
TUTOPLAST PROCESS
Overall the structure, biomechanics and remodeling characteristics of the implant are maintained.
THOROUGHLY PENETRATES TISSUE
Osmotic treatments disrupt cell membranes to allow for full penetration of the graft.
VALIDATED VIRAL INACTIVATION
- Ability to inactivate or remove HIV, hepatitis, fungi, and spores
- Validated by individual tissue type based on most difficult case testing using most difficult to kill organisms
Osmotic, oxidative and alkaline (if indicated) treatments break down cell walls, inactivate pathogens, and remove bacteria.
Solvent dehydration allows for room-temperature storage of tissue without damaging the native tissue structure.
Low-dose gamma irradiation ensures a sterility level (SAL) of 10-6 of the final packaged graft.
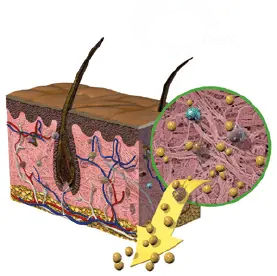
1. Alkaline Treatment
Removes cells and lipids which
interfere with healing.
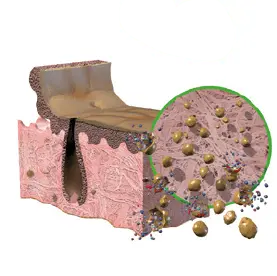
2. Osmotic Treatment
Disrupts cell membranes to allow easier
removal of cellular components.
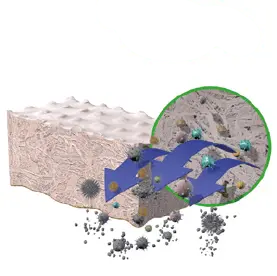
3. Oxidative Treatment
Inactivates pathogens and removes
bacteria.

4. Solvent Treatment
Removes water from tissue, preserves the natural
tissue matrix and allows for room-temperature
storage without damaging the native structure.

5. IRRADIATION
Low-dose irradiation produces a terminally sterile
graft, while preserving structural integrity.

PRE-PROCESSED HUMAN DERMIS
Note presence of intact epidermis.

TUTOPLAST PROCESSED HUMAN DERMIS
Note epidermis has been removed and underlying matrix has been preserved.
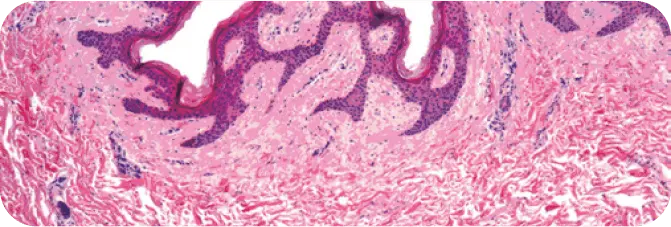
PRE-PROCESSED HUMAN DERMIS
Note the presence of cellular debris throughout (purple cell nuclei).
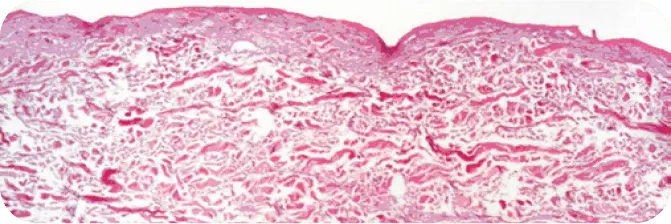
TUTOPLAST PROCESSED HUMAN DERMIS
Note the absence of cellular debris and the intact tissue matrix.
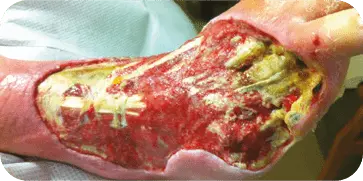
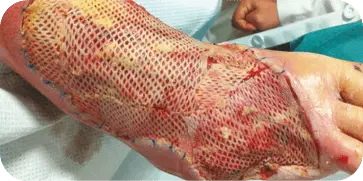
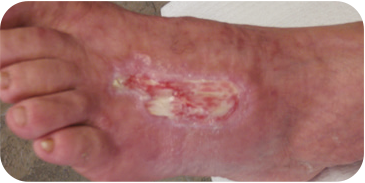
DIABETIC FOOT ULCER
Patient presented with a diabetic ulcer with exposed tendon and bone on
the dorsal aspect of the foot. The surgeon used multiple grafts to cover the
entire surface of the wound. At three weeks the wound showed a decrease in
wound depth and significant granulation tissue present.
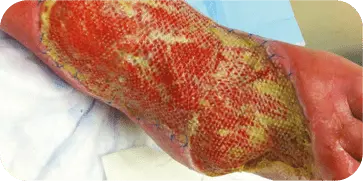
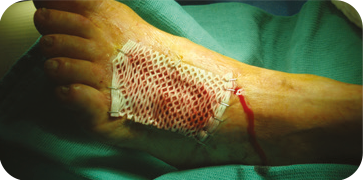
INSECT BITE
Patient presented with an infected insect bite with exposed tendon and
bone on the dorsal aspect of the foot. The wound required two graft
applications. At 10 weeks the wound showed 70 percent decrease in size
and 80 percent granulation tissue coverage.
The donated human tissue source of Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix produces a biocompatible intact porous
scaffold to support cellular proliferation and revascularization. The Tutoplast Process preserves the key
components of the native matrix that support the body’s regenerative processes.
IN-VIVO ANIMAL MODEL STUDY*
The graft functioned successfully as a scaffold and is fully incorporated and remodeled by the host tissue.
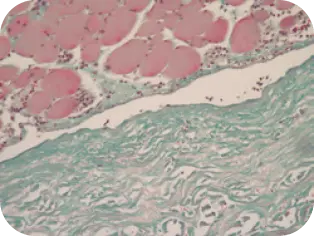
DAY 1
Beginning of cellular infiltration
of the graft by host tissue.
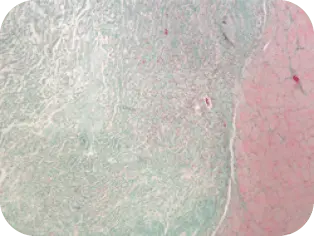
DAY 7
Vascularization evident, invasion
of fibroblasts and other cells
found in normal healing cascade
of the graft by host tissue.
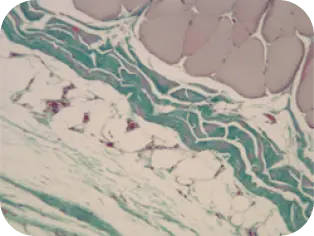
WEEK 8
Difficult to distinguish implant
from host tissue; graft is well
incorporated.
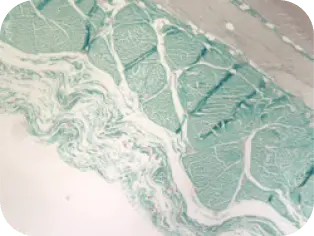
WEEK 16
Beginning of cellular infiltration
of the graft by host tissue.
*Performance data from animal studies may not be representative of performance in humans.
HCPCS CODE FOR Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) assigned a brand-specific Level II HCPCS code, Q4238, to Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix.
CMS has indicated that these brand-specific HCPCS codes are applicable for all sites of service that use the Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix.
CODE DESCRIPTION
Q4238 Derm-Maxx™, per square cm
Use of the HCPCS Q-code does not guarantee payment. You should select the most appropriate codes for the procedures performed. Coding practices will vary by the site of care, patient condition, range of services provided, local carrier instructions, and other factors. The decision about how to complete a reimbursement claim form, including billing amounts, is exclusively the responsibility of the provider. Coding regulations are subject to change at any time.
ORDERING INFORMATION
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| MDRM-11 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 1cm x 1cm |
| MDRM-22 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 2cm x 2cm |
| MDRM-24 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 2cm x 4cm |
| MDRM-44 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 4cm x 4cm |
| MDRM-48 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 4cm x 8cm |
| MDRM-510 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 5cmx10cm |
| MDRM-816 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 8cmx16cm |
| MDRM-11 | Derm-Maxx™ Dermal Matrix 2cm x 2cm |